Python Lamda Functions. No-name. One-line functions
Lamda function is a small function having just one expression and written in just one line. They don’t need any function name. They are very handy when you need a small one-line code.
Lamda functions always start with lamda
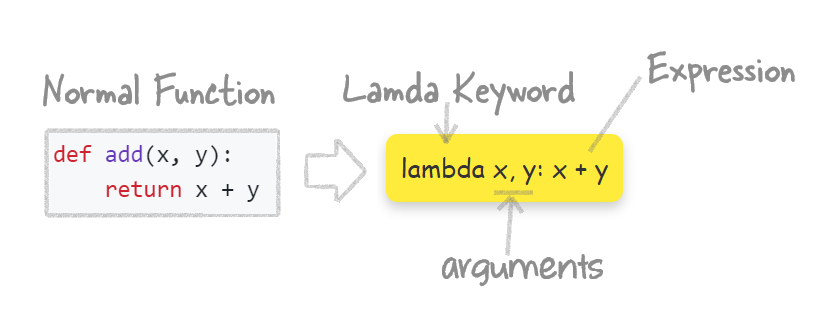
What is Lambda?
A lambda function is a small function you write in one line, without even naming it. Here is how a normal function and its lamda counterpart would look like:
Where to Use Lambda
Lambda functions are handy for small, quick tasks where you don’t need a full function. Here are a few places where they are commonly used:
1. Sorting with Custom Rules
Let’s say you have a list of names and you want to sort them by length instead of alphabetically. Normally, you would write a function, but with a lambda, it’s easy:
names = ['Rahul', 'Amit', 'Zara', 'Pooja']
sorted_names = sorted(names, key=lambda x: len(x))
Use lambda for sorting lists in a custom way.
2. Filtering Lists
If you have a list of numbers and you only want the even ones, lambda makes it easy:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
even_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
Lambda functions are perfect for filtering lists.
3. Mapping Data
Let’s say you want to double every number in a list. Instead of writing a loop, you can use map() with a lambda:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
doubled = list(map(lambda x: x * 2, numbers))
Use lambda to quickly transform data in lists.
4. Filtering with Lambda
If you need to filter out items from a list based on a condition, filter with a lambda function is a quick solution:
numbers = [5, 12, 17, 24, 29]
filtered_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x > 15, numbers))
Lambda is great for filtering lists based on specific conditions.
5. Applying Lambda to a DataFrame
When working with data, you can use apply with a lambda function to perform operations on each element in a DataFrame column:
df['new_column'] = df['existing_column'].apply(lambda x: x + 10)
Apply lambda functions to DataFrame columns for quick data manipulation.
6. Combining Lambda with List Comprehensions
Sometimes, you might want to use a lambda function within a list comprehension for more complex operations:
result = [(lambda x: x * 2)(x) for x in range(5)]
Combine lambda functions with list comprehensions.
7. Lamda with IF-ELIF-ELSE
You can use a lambda function to quickly check if a number is odd or even:
odd_even_lambda = lambda i: 'Number is Even' if i % 2 == 0 else 'Number is Odd'
You can use lamda with if IF-ELIF-ELSE logic
Let’s recap
Don’t expect lambda functions to shrink your entire code. They’re only meant for small, one-line tasks where you don’t need to name the function.