Getting started with git¶
Every project needs a version control. Git is simply a version control software. There are other version control software like Mercurial, Subversion, Visual Source Safe, etc. But git is the most popular one. It is free and open source. And if you use GitHub, or GitLab, or BitBucket or Azure DevOps, you are using git already.
git is distributed¶
Git is a distributed version control system. This means that every developer has a complete copy of the repository on their local machine. This allows developers to work offline, commit changes, and then push those changes to the remote repository when they are ready.
git init¶
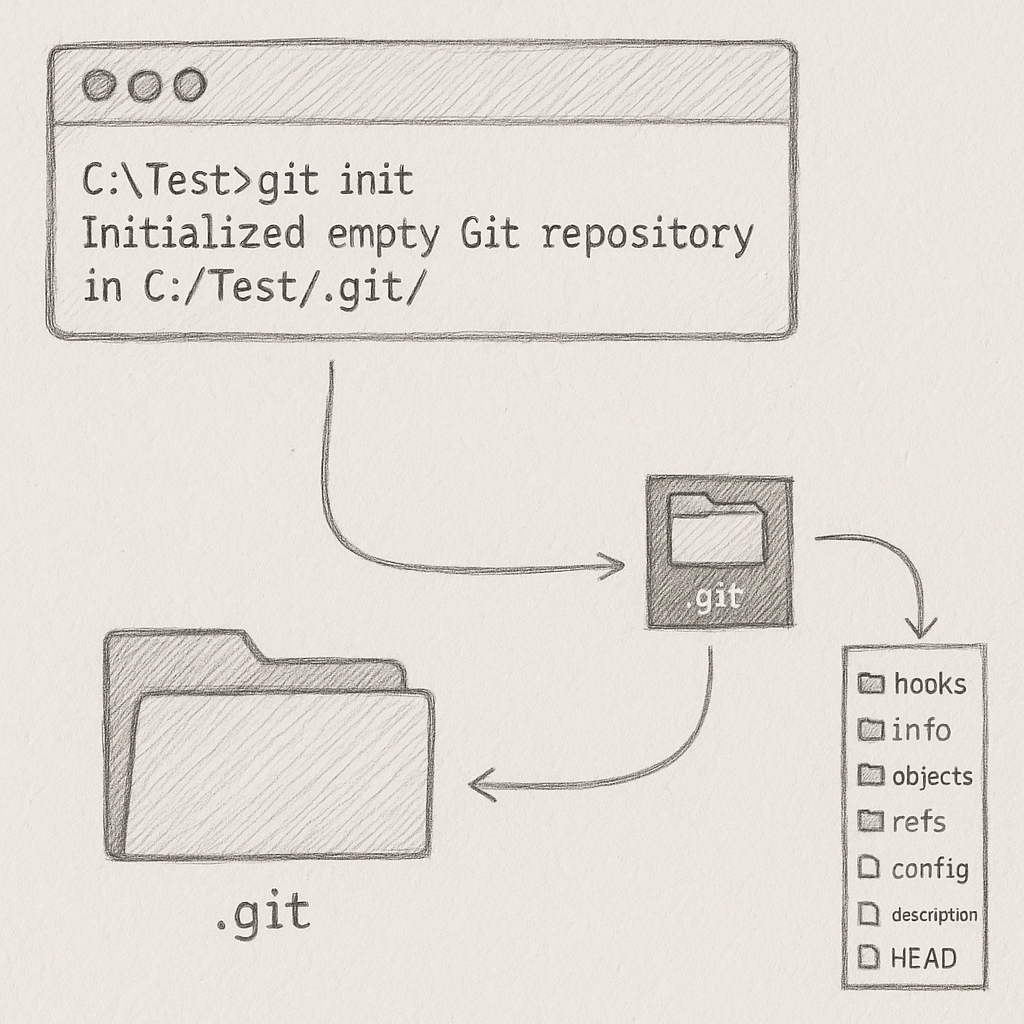
The first thing you do to use git is to install the git software. CD to the root folder of your project and then run git init . This will create a hidden .git folder inside the root folder of your project. This .git folder is the git repository. It is the central database/vault that git uses to track all git activities
But, wait, do we use git init nowadays? No, in real-world we dont. git clone does it all - sets up .git folder, remote origin, copies files, everything. But, for that coding ninja who want to do it all by hand, he will first run git init, then git remote add origin git pull to pull the latest changes from the remote repo, and finally git push to push the changes to the remote repo.
The .git folder¶
The .git folder is the central vault of git. Everything related to git is stored in this one folder. There is nothing outside it. It is a hidden folder.
git clone¶
A super popular command every developer uses at the start of a project is git clone <some-url>. On a very high level, it just clones(copies) the files from the remote repository to your local folder.
What happens when you run git clone <some-url>?¶
When you run git clone <some-url>, it does the following things:
- First it creates an empty folder in your current directory with the same name as the remote repository. For example, if you run
git clone https://github.com/france/paris.git, it will create a folder calledparisin your current directory. - Inside this new directory, Git initializes a fresh .git folder.
- Then it extracts all the latest source code files from the
.gitfolder into the empty folder. - Git downloads all the repository’s data (commits, branches, tags, and history) from the remote server and stores it inside your new local .git folder.
- Git checks out the default branch (usually main or master) and unpacks the latest files from that branch into your working directory.
How does git know which is the default branch?
Git uses the remote repository's HEAD reference to determine the default branch. When you clone a repository, Git fetches the HEAD reference from the remote server, which points to the default branch. This is usually set to main or master, but it can be configured differently in the remote repository settings. If you want to check out a different branch, you can do it by using the --branch option in the git clone command, like this: git clone -b <branch-name> <some-url>.
Note
The remote server does not send you a pre-made .git folder; it sends the repository data, and Git builds the .git folder on your machine.
What if you dont want to use the clone command?
- First you need to run
git initin your project folder. - Then you need to run
git remote add origin <remote-repo-url>to add the remote repository as "origin". - Then you need to
git fetch originto fetch the latest changes from the remote repository. - Finally, you can run
git checkout mainto check out the default branch. - But, wait, you also need to run
git branch --track <branch-name> origin/<branch-name>for each branch you want to track.
Some dumb questions¶
-
What if I run
git initin my project again?Just git init again? No url?
-
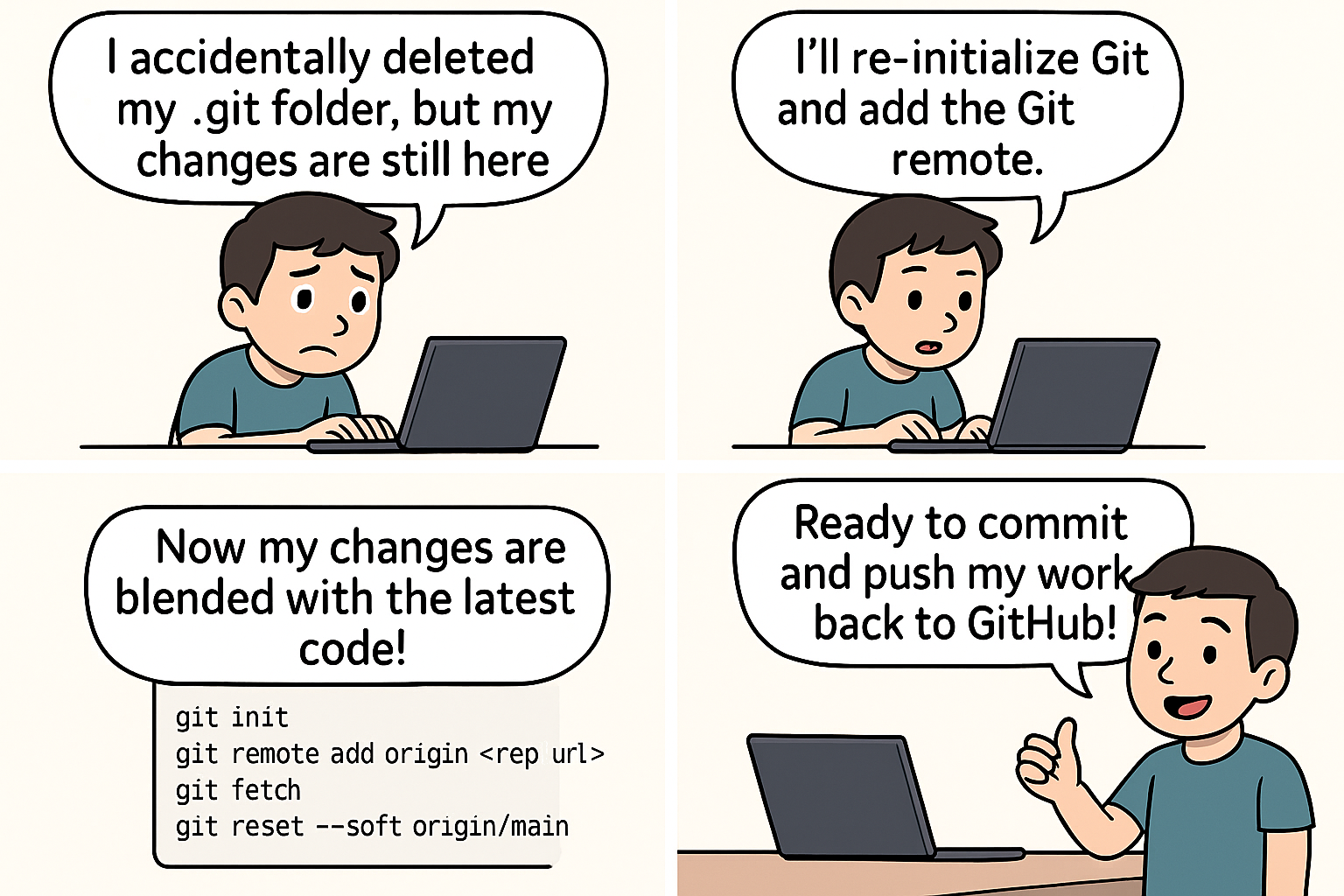
What if I delete the
.gitfolder?Nothing will happen to your project files. They will be untouched. But, that .git folder is the central database for all things git. Hence, you will lose all your git history, commits, branches, and everything related to git. Your project will no longer be a git repository. You were most centernaly connected to either Github. You will need to do some workarounds to get everything back to normal.